CYBER CRIME Vs CYBER TERRORISM

CYBER CRIME Vs CYBER TERRORISM
CYBER CRIME
Cyber-crime is a crime committed on a computer network though it constitutes traditional crimes like theft, extortion, harassment, vandalism and trespassing. Other traditional crimes like rape, bigamy, homicide cannot occur online as it requires physical activity.

Traditionally, every state exercises
its sovereign power to maintain internal
and external order. In order to maintain
internal order, the states have evolved
criminal rules to maintain and protect
the life and the property of its citizens.

To maintain the external order states relied
on international agreements and military force.
Computer technology has created new class
of threats called cyber-threats. This kind of threat
is generated by using computer technology to
undermine the state’s ability maintain
internal and external order.
Jurisdiction forms an integral part of criminal jurisprudence. Computer generated crimes erodes the territorial jurisdiction. Virtual attacks can be generated from any part of the world and in turn any part of the world can become a subject to these cyber attacks.
Database of any hospital can be hacked and can kill the people by altering the dosage of their medication. This kind of crime may not be deducted at alland the deaths can be put as negligence on the part of the hospital.

DDoS – distributed denial of service is extensively used for extortion by employing new method by launching an attack on website and the hackers demand ransom to stop the attack. This forms a new method to commission old type of crime of extortion. In 2000 when Amazon, e-bay etc became a victim of DDoSit can be defined as a pure cyber crime.
Computers can also be used to forge documents, make counterfeit currency etc.Cybercrime can safely be described the use of computer technology to commit crimes i.e. to engage in activity which threatens the State to maintain its internal order.
CYBER TERRORISM
FBI defines cyber terrorism as any premeditated, politically motivatedattack against information systems, programs and data that threatens violence or result in violence against noncombatant’s targets by subnational groups or clandestine agents.
Physical harm is not always considered a prerequisite for classifying a cyber attack as a terrorist event. The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, known as NATO, has defined cyber terrorism as a cyber attack that uses or exploits computer or communication networks to cause “sufficient destruction or disruption to generate fear or to intimidate a society into an ideological goal.”
Attackers often do this by damaging or disrupting critical infrastructure. It essentially means to use computer technology to engage in terrorism. The difference between crime and terrorism is that though the crime is personal in nature while terrorism is political in nature. Crimes are committed to individual personal reasons which are for personal gains and the desire to harm others physically and psychologically.
Terrorism results in infliction of harm as it coerce a civilian population to influence government policies by intimidation or coercion or to affect the conduct of government by mass destruction, assassination or kidnapping. Terrorism achieves its goal by demoralizing the civilians by destroying property, injuring or killing civilians.
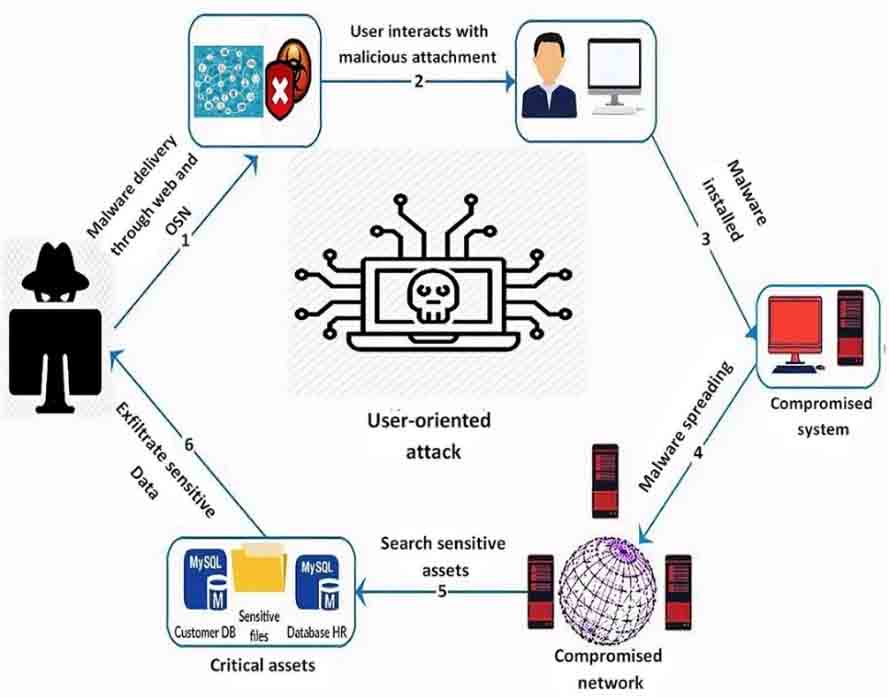
METHODS OF CYBER-TERRORISM
- ADVANCED PERSISTENT THREAT (APT) – National Defense, manufacturing and financial industry are typical targets of cyber- terrorism. They use sophisticated and concentrated penetration methods to gain network access. The attackers stay undedicated for a period of time with the intension of stealing data.
- COMPUTER VIRUSES, WORMS & MALWARE – they control IT control systems, they attack utilities, transportation system, power grids, critical infrastructure and military systems.
- DISRIBUTED DENIAL OF SERVICE (DDoS)- the legitimate users are prevented from using and accessing their computers systems, devises and network.

- HACKING– gaining unauthorized access, seeks to steal critical data.

- RANSOMWARE – type of malware, holds data or information system hostage unless the victim pays a ransom.
- PHISHING – attempt to collect information through a target’s email, using that information to access system or to steal the victim’s identity.
Instances of cyber terrorism–
- Hackers with ties to the Chinese government deployed ransom ware attacks against five major gaming companies. They demanded over $100 million in ransom.
-

The Polish government said it suspected Russian
hackers had taken control of Poland’s National Atomic
Energy Agency and Health Ministry websites for a short time. They tried to spread alarms about a radioactive threat that didn’t exist.

- Brazilian hackers attacked a website belonging to Indonesia’s State Cyber and Password Agency.
We become more connected and reliant on technology, we become more vulnerable to cyber attacks. If you know that you are the victim of a cyber-attack, or if you know that an attack has occurred, you should take actions to ensure that your personal data is protected. Check to make sure the software on all of your systems is up-to-date. Run a scan to make sure your system is not infected or acting suspiciously. If you find a problem, disconnect your device from the Internet and perform a full system restore.
